Blue-headed Crested Flycatcher Trochocercus nitens Scientific name definitions
Text last updated December 4, 2017
Sign in to see your badges
Species names in all available languages
| Language | Common name |
|---|---|
| Catalan | monarca crestat occidental |
| Dutch | Blauwkopkuifmonarch |
| English | Blue-headed Crested Flycatcher |
| English (South Africa) | Blue-headed Crested Flycatcher |
| English (United States) | Blue-headed Crested Flycatcher |
| French | Tchitrec noir |
| French (France) | Tchitrec noir |
| German | Schwarzkopfmonarch |
| Japanese | アオカンムリヒタキ |
| Norwegian | blåhodemonark |
| Polish | muchodławka stalowa |
| Portuguese (Angola) | Papa-moscas-de-poupa-de-capuz-azulado |
| Russian | Чубатый монарх |
| Serbian | Plavoglava ćubasta muharica |
| Slovak | vípkar chochlatý |
| Spanish | Monarca Brillante |
| Spanish (Spain) | Monarca brillante |
| Swedish | blåhuvad monark |
| Turkish | Lacivert Tepeli Monark |
| Ukrainian | Монарх західний |
Trochocercus nitens Cassin, 1859
Definitions
- TROCHOCERCUS
- nitens
The Key to Scientific Names
Legend Overview
Field Identification
15 cm; 11·8 g. Has short but obvious crest, graduated tail. Male nominate race is wholly glossy blackish-blue above and to breast, with clearly delimited (by thin white line) and contrasting grey from lower breast to undertail-coverts; flight-feathers brownish-black; iris brown; bill blue-grey, upper mandible blacker, mouth yellow; legs blue-grey to blackish-brown. Female has crest shorter than male’s, glossy blackish-blue restricted to crown, upperparts dark slate-grey with faint bluish tinge, flight-feathers dark brown-grey, throat and underparts entirely grey; bill dark slate-grey, upper mandible blacker, mouth greenish, legs dark brown. Juvenile is like female but duller; immature male like female but head side, throat and upper breast speckled pale grey. Race reichenowi has underparts darker grey than nominate.
Systematics History
Editor's Note: This article requires further editing work to merge existing content into the appropriate Subspecies sections. Please bear with us while this update takes place.
Two subspecies recognized.Subspecies
Trochocercus nitens reichenowi Scientific name definitions
Distribution
Trochocercus nitens reichenowi Sharpe, 1904
Definitions
- TROCHOCERCUS
- nitens
- reichenovi / reichenovii / reichenowi
The Key to Scientific Names
Legend Overview
Trochocercus nitens nitens Scientific name definitions
Distribution
Trochocercus nitens nitens Cassin, 1859
Definitions
- TROCHOCERCUS
- nitens
The Key to Scientific Names
Legend Overview
Distribution
Editor's Note: Additional distribution information for this taxon can be found in the 'Subspecies' article above. In the future we will develop a range-wide distribution article.
Habitat
Movement
Diet and Foraging
Sounds and Vocal Behavior
Song a fast, long, far-carrying, hollow “hohohohohohohoho…” , often introduced (in conflicts) by some harsh notes or a dry, excited “tictictictictictic” rattle. Call a harsh “zwhee-zwheh” or “tchitt-tchitt”.
Breeding
Conservation Status
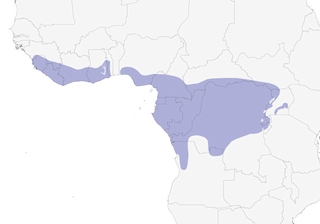
- Year-round
- Migration
- Breeding
- Non-Breeding




























