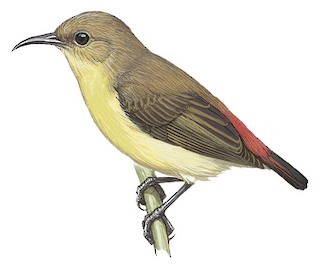
Crimson-backed Sunbird Leptocoma minima Scientific name definitions
- LC Least Concern
- Names (21)
- Monotypic
Text last updated February 7, 2013
Sign in to see your badges
Species names in all available languages
| Language | Common name |
|---|---|
| Catalan | suimanga menut |
| Dutch | Dwerghoningzuiger |
| English | Crimson-backed Sunbird |
| English (India) | Crimson-backed Sunbird (Small Sunbird) |
| English (United States) | Crimson-backed Sunbird |
| French | Souimanga menu |
| French (France) | Souimanga menu |
| German | Däumlingsnektarvogel |
| Icelandic | Dvergsólfugl |
| Japanese | マメタイヨウチョウ |
| Malayalam | ചെറുതേൻകിളി |
| Marathi | छोटा शिंजीर |
| Norwegian | malabarsolfugl |
| Polish | nektarnik mały |
| Russian | Карликовая нектарница |
| Slovak | nektárovka malá |
| Spanish | Suimanga Mínimo |
| Spanish (Spain) | Suimanga mínimo |
| Swedish | ghatssolfågel |
| Turkish | Al Sırtlı Nektarkuşu |
| Ukrainian | Нектаринка мала |
Leptocoma minima (Sykes, 1832)
Definitions
- LEPTOCOMA
- minima / minimum / minimus
The Key to Scientific Names
Legend Overview
Field Identification
8 cm; male 4–6 g, female 4–5 g. Very small. Male breeding has crown iridescent green , side of face blackish, upperwing and tail blackish-brown with lilac gloss, back and shoulder deep red, and rump metallic purple or lilac; purple throat, crimson upper breast bordered with blackish band below, dull yellow belly, bright lemon pectoral tufts, greyish-white flanks; iris dark brown; bill and legs blackish. Male in non-breeding plumage (Apr/May–Aug) is similar to female, but brighter olive on head, with back and shoulders metallic red, rump and uppertail-coverts metallic purple; lesser upperwing-coverts metallic red, forming with adjacent part of back a broad band. Female is olive above, with lower rump and uppertail-coverts deep maroon-crimson, remiges edged brown and olive, dull yellow below; iris dark brown, bill and legs blackish but paler than male, particularly at base of lower mandible. Juvenile resembles female but greyer, with duller red rump, more yellow below.
Systematics History
Subspecies
Distribution
Western Ghats (from N of Mumbai, S to hills of S Kerala), in W India.
Habitat
Movement
Diet and Foraging
Insects, spiders (Araneae) and nectar . Forages singly, in pairs or in small groups. Active and acrobatic; clings upside-down to plants, also hovers. Defends flowering trees against conspecifics, also against flowerpeckers (Dicaeidae).
Sounds and Vocal Behavior
Breeding
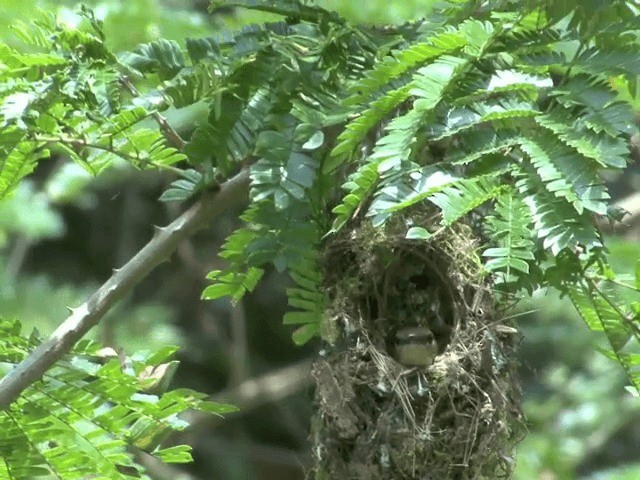
Laying recorded in Feb–Mar, May and Dec in Mumbai area, Sept–Apr in Kerala but May–Oct in Nilgiris. Nest a neat, rounded, hanging pouch of fibres, moss and cobwebs, suspended from tip of twig within 2 m of ground in bush or sapling, commonly on Strobilanthes plant, on edge of path or clearing. Clutch 2 eggs; white with dense ring of reddish spots, and speckled reddish. No other information.
Conservation Status
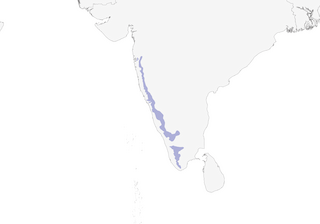
- Year-round
- Migration
- Breeding
- Non-Breeding