Fiji Woodswallow Artamus mentalis Scientific name definitions
- LC Least Concern
- Names (18)
- Monotypic
Text last updated May 15, 2014
Sign in to see your badges
Species names in all available languages
| Language | Common name |
|---|---|
| Catalan | àrtam de les Fiji |
| Dutch | Fijispitsvogel |
| English | Fiji Woodswallow |
| English (United States) | Fiji Woodswallow |
| French | Langrayen des Fidji |
| French (France) | Langrayen des Fidji |
| German | Fidschischwalbenstar |
| Japanese | フィジーモリツバメ |
| Norwegian | fijisvalestær |
| Polish | ostrolot białogardły |
| Russian | Фиджийский артам |
| Serbian | Šumska lasta sa Fidžija |
| Slovak | hmyziar bieloprsý |
| Spanish | Artamo de las Fiyi |
| Spanish (Spain) | Artamo de las Fiyi |
| Swedish | fijisvalstare |
| Turkish | Fiji Ormankırlangıcı |
| Ukrainian | Ланграйн фіджійський |
Artamus mentalis Jardine, 1845
Definitions
- ARTAMUS
- mentale / mentalis
The Key to Scientific Names
Legend Overview
Field Identification
17 cm; 33–48 g. Head to chin, upperparts and wing are black, except for white rump and uppertail-coverts; tail black with white tip ; underparts white, extending up over lower throat onto central ear-coverts; iris dark brown; bill pale blue-grey, tip black; legs grey. Differs from White-breasted Woodswallow (Artamus leucorynchus) in having white (not black) lower throat and central ear-coverts, separated irregularly (not evenly) from black colour of head. Sexes alike. Juvenile is similar to adult, but with paler feather edgings above.
Systematics History
Sometimes treated as conspecific with Artamus leucorynchus, but differs in plumage and voice. Monotypic.
Subspecies
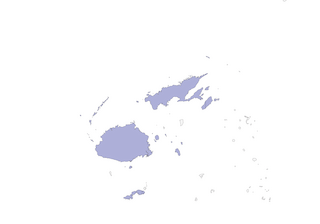
Distribution
W & N Fiji Is: Yasawa Group, Viti Levu, Vanua Levu, Taveuni, Gau and Kadavu (at least formerly also Koro, Yasayamoala and N Lau Group (1) ).
Habitat
Movement
Diet and Foraging
Insectivorous . Impressive aerial forager, with fast pursuit-flight. Seizes prey in aerial sally launched from conspicuous perch; occasionally pounces on items near ground; will also make sweeps over flowering plants, and snap at insects. Smaller items swallowed whole; large prey taken back to perch and dismembered before being consumed.
Sounds and Vocal Behavior
Breeding
Conservation Status
- Year-round
- Migration
- Breeding
- Non-Breeding
































