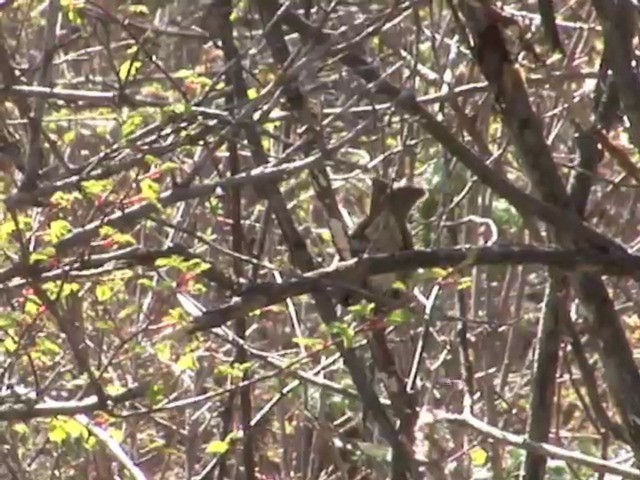
Three-banded Rosefinch Carpodacus trifasciatus Scientific name definitions
- LC Least Concern
- Names (19)
- Monotypic
Text last updated June 26, 2013
Sign in to see your badges
Species names in all available languages
| Language | Common name |
|---|---|
| Catalan | pinsà rosat de tres bandes |
| Chinese (SIM) | 斑翅朱雀 |
| Dutch | Witbuikroodmus |
| English | Three-banded Rosefinch |
| English (United States) | Three-banded Rosefinch |
| French | Roselin à trois bandes |
| French (France) | Roselin à trois bandes |
| German | Bindengimpel |
| Japanese | ミスジマシコ |
| Norwegian | blodrosenfink |
| Polish | dziwonia czarnolica |
| Russian | Полосатокрылая чечевица |
| Serbian | Tropruga rumenka |
| Slovak | červenák čiernolíci |
| Spanish | Camachuelo Tribarrado |
| Spanish (Spain) | Camachuelo tribarrado |
| Swedish | vitbukig rosenfink |
| Turkish | Üç Renkli Çütre |
| Ukrainian | Чечевиця темнощока |
Carpodacus trifasciatus Verreaux, 1871
Definitions
- CARPODACUS
- trifasciata / trifasciatus
The Key to Scientific Names
Legend Overview
Field Identification
17–19·5 cm. Large and large-billed, robust rosefinch with broad wingbars and long tail. Male has white forehead edged light crimson, crown to nape and side of neck deep crimson, finely or lightly streaked (dark feather bases); lores, cheek and upper ear-coverts black, suffused with crimson, lower ear-coverts crimson, cheek finely spotted and ear-coverts finely streaked white; mantle, back and scapulars dark carmine or crimson, streaked black (upper mantle sometimes grey), outer scapulars broadly tipped white (forming broad band), rump and uppertail-coverts unstreaked crimson, longest coverts dark grey; tail and upperwing black, median and greater coverts broadly tipped pinkish-white or white (forming two broad wingbars), tertials broadly edged and tipped white; chin and throat blackish, tipped buff or finely white (usually only on side of throat), breast and flanks deep crimson, tipped blackish, side of breast (beside bend of wing) pale grey, rest of underparts white; iris brown; bill greenish-yellow to yellowish-horn, culmen and tip darker horn; legs dark brown or reddish-brown. Female has forehead to nape, face and upperparts light olive-brown, streaked blackish or greyish on mantle, outer scapulars broadly edged yellowish-buff or whitish; tail and wing much as on male, median and greater coverts dark grey, broadly tipped yellowish-buff or fawn, tertials broadly edged and tipped whitish or yellowish-white; chin and throat whitish or dull yellowish, sometimes indistinct dark olive malar stripe, breast and flanks light olive-buff, tinged yellow and indistinctly streaked duller, side of breast pale grey, lower flanks washed paler buff, belly to undertail-coverts pale greyish or white; bill brownish-horn above, yellowish-brown below. Juvenile is like female, but slightly duller or browner; first-winter male has outer scapulars yellowish-white, tips of median coverts light orange-yellow, greaters tipped yellow, rump olive or light reddish-brown, face darker (similar to adult male) with whitish tips on ear-coverts, breast and flanks warm rust-brown, bill as adult female but more yellow at base of both mandibles; first-summer male darker brown crown and upperparts except for greyish mantle, tips of median and greater coverts pale buff or whitish-buff, side of breast and flanks pale greyish or greyish-white, streaked blackish.
Systematics History
Subspecies
Distribution
SC China from S Gansu and S Shaanxi S to E Tibet, NW Yunnan and W Sichuan; non-breeding also SE Tibet, possibly also NE Indian Subcontinent.
Habitat
Found in undergrowth and thickets of conifer forest, juniper (Juniperus) thickets, spruce (Picea), locally thickets of birch (Betula) and willow (Salix) e.g. in S Gansu, between c. 2100 m (occasionally lower) and 3050 m. In winter at lower level, down to 1800 m, at edges of cultivation, orchards, hedges, bushes, particularly cotoneaster (Cotoneaster) bushes, areas with crab apples (Malus) and open cereal fields.
Movement
Resident, partial migrant and altitudinal migrant. In non-breeding season moves to lower levels, including foothills and valleys, but some remain at high altitudes until forced to move by severe weather; winters mostly within breeding range, also S to SE Tibet. Return movements from mid-Mar. Recorded as a vagrant in NE India (Arunachal Pradesh) and Bhutan, where possibly a scarce or local visitor to some N valleys.
Diet and Foraging
Mainly seeds, also some fruit, including crab apples and cotoneaster berries; also willow buds on migration to breeding grounds. Forages on the ground and in bushes; generally sluggish or slow-moving when on ground. Often spends long periods perched motionless in undergrowth or bushes. In pairs and small groups.
Sounds and Vocal Behavior
No information; generally silent. Captive individuals gave weak and high-pitched calls.
Breeding
No confirmed information. Unconfirmed report, based on information from 1925: nest cup-shaped, made of roots and twigs, lined with grasses, rootlets, hair and wool, placed low down in bush or fairly high up in conifer; 3–5 eggs, blue with brown markings.
Conservation Status
Not globally threatened. Uncommon to scarce; locally common in non-breeding season in S China. Area occupied during breeding season apparently much smaller in extent than previously believed. If this is true, the species' conservation status may merit reassessment, perhaps as Near-threatened or even Vulnerable.
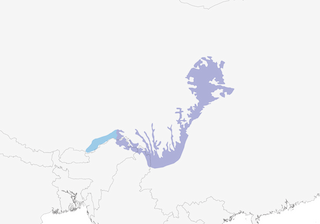
- Year-round
- Migration
- Breeding
- Non-Breeding






























